HOW TO CHOOSE THE CORRECT WATER-FILLED BARRIERS FOR YOUR SITE?
Choosing the right water-filled barriers starts with one key question: where will they be used?
Whether you need to create safe pedestrian walkways, separate pedestrians from vehicle traffic, or provide roadside separation, water-filled barriers can be deployed in a range of environments, and the best option depends on your application.
In this article, we’ll outline the most common use cases for water-filled barriers, explain the three main barrier types, and help you identify which option is right for your site.
WHAT ARE WATER-FILLED BARRIER USED FOR?
Water-filled barriers are used to create a clear separation to allow safe movement for pedestrians and vehicles. The three most common use cases can be divided in three groups:
-
Pedestrian control and walkways:
Used to guide foot traffic, create temporary walkways, and define low-risk pedestrian-only zones, often on construction sites or at events.
-
Pedestrian–vehicle separation:
Used where people and vehicles are in close proximity, such as in busy city centres. In these environments, the risks for accidents are higher and stronger physical separation is required.
-
Roadside separation:
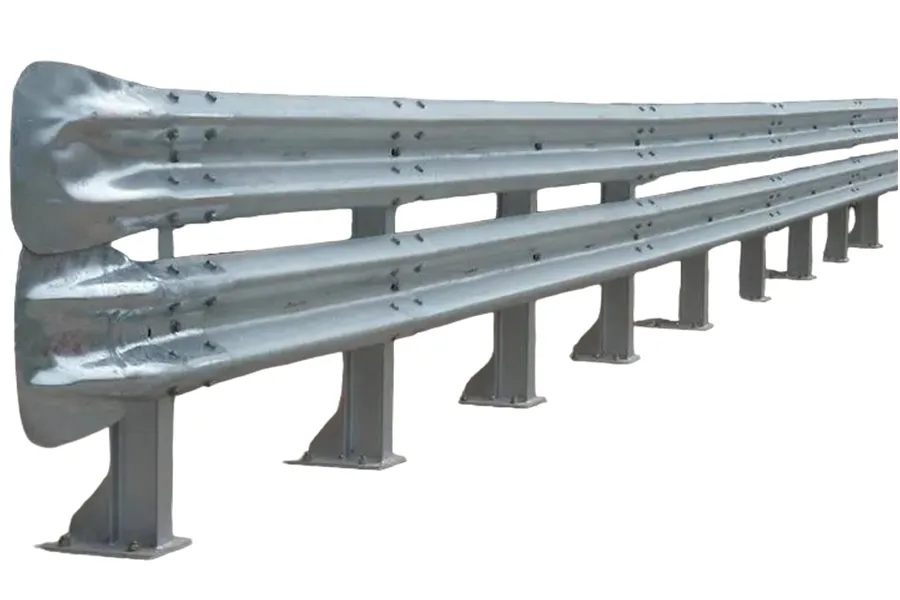
Used along roads or in high-speed environments where there is a risk of vehicle impact. Application in these high-risk environments typically requires barriers that are crash-tested and certified for the intended use.
WHICH BARRIER IS SUITABLE FOR EACH USE CASE?
There is a suitable water-filled barrier for each of these use cases:
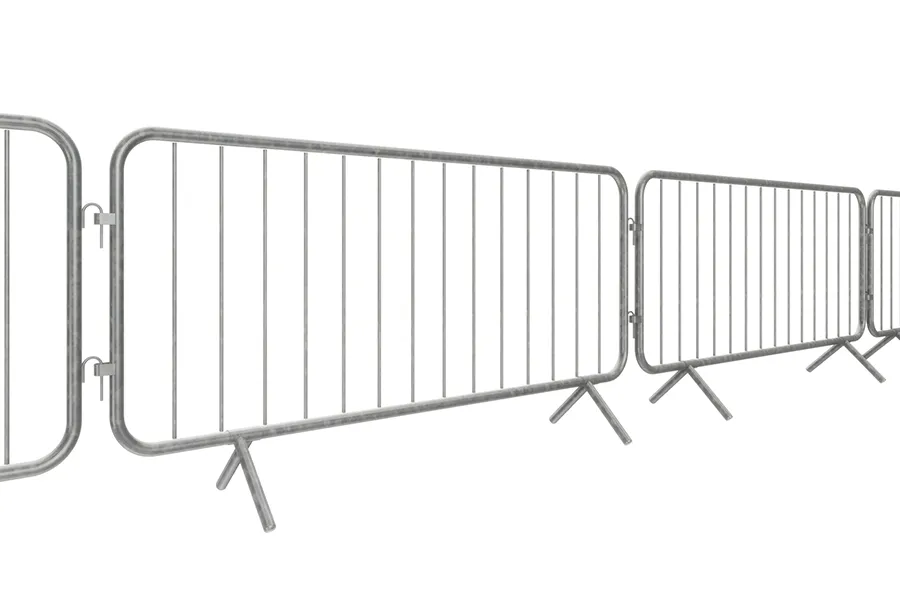
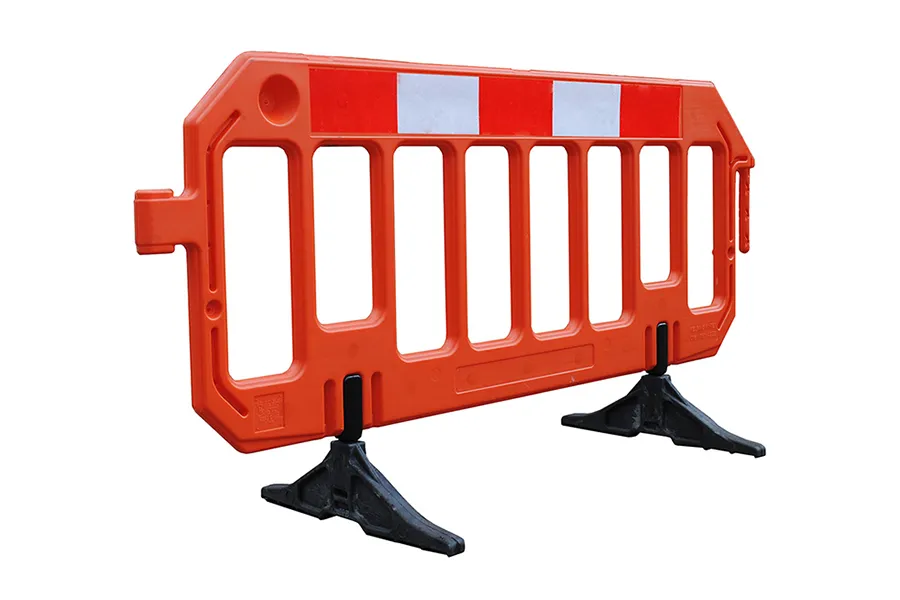
- Light-duty barriers are used lower risk areas, often to create pedestrian walkways.
- Heavy-duty barriers are used in areas where traffic is lower, but security needs are higher, such as sites in busy city centres.
- Heavy-duty, crash-tested barriers are designed for high-risk areas such as roadside construction sites.
WHAT'S THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE THREE BARRIER TYPES?
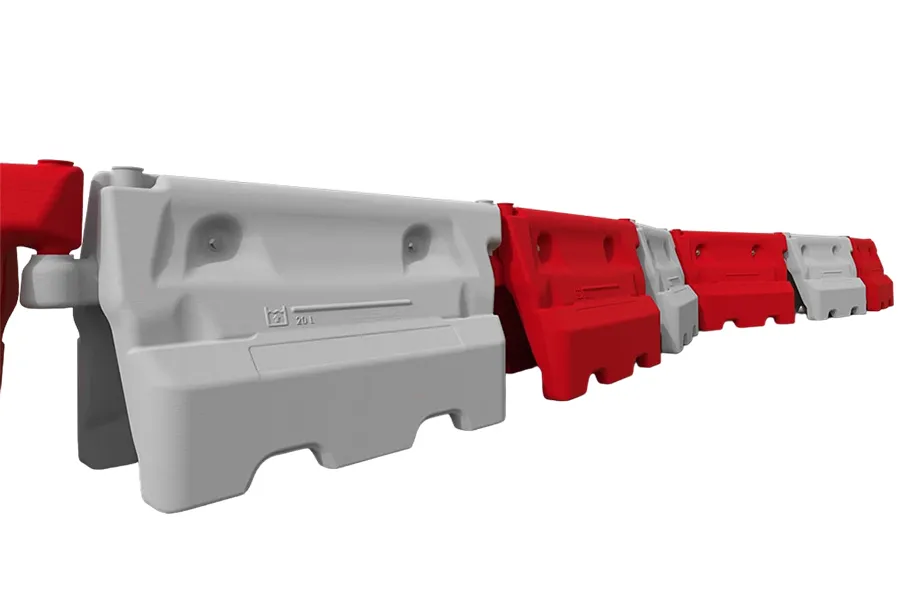
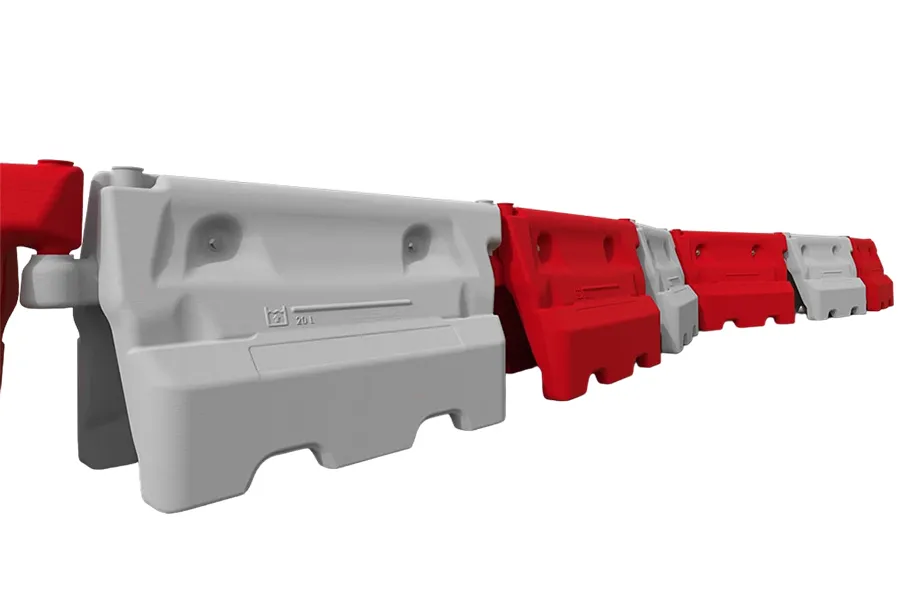
- Light-duty barriers
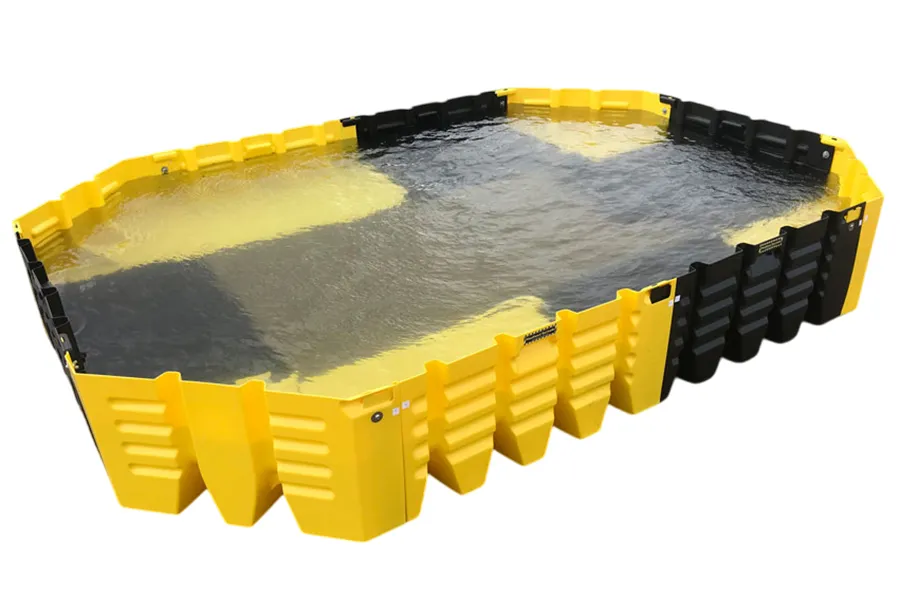
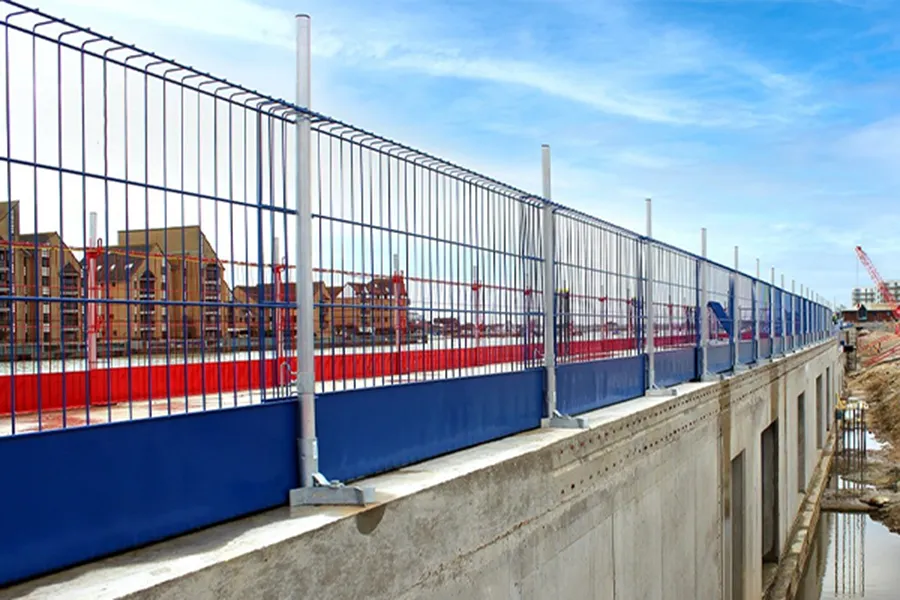
Light-duty water-filled barriers are around 1m in length and have a lower water capacity than the heavy-duty options. They can be fitted with mesh fence extensions to increase their height and therefore security. - Heavy-duty barriers
Heavy-duty water-filled barriers are typically around 2m in length and can take significantly more water than the 1m versions. They can be used with hoarding extensions to increase security.
Barrier type
Length
Width
Height
Material
Water capacity
Crash-tested?
Best suited for
Light-duty barriers
800mm-1.5m
400-800mm
555mm-800mm
HDPE
20-55L
No
Pedestrian control and walkways
Heavy-duty barriers
2m +
350mm-550mm
800mm-1m
HDPE
155L-540L
No
Pedestrian–vehicle separation
Heavy-duty, crash-tested barriers
2m +
350mm-550mm
800mm-1m
HDPE
155L-540L
Yes
Roadside application
- Heavy-duty, crash-tested barriers
Crash-tested barriers are best suited to higher-risk environments, such as motorways or sites with higher vehicle speeds. Because crash-tested requirements can vary by application, it’s important to confirm your site’s needs and verify the barrier’s relevant certifications before purchasing.
Conclusion
To choose the correct water-filled barriers for your site, start with where and how they’ll be used: pedestrian walkways, pedestrian and vehicle separation, or high-traffic environments. Then match the required height and duty type: 1m barriers for pedestrian control, and 2m barriers when stronger separation, access control, or vehicle management is needed.
Not sure which barrier type to choose? Tell us more about your site environment and we’ll recommend the right option.







































































































































 HERMEQ UK
HERMEQ UK HERMEQ Ireland
HERMEQ Ireland HERMEQ Netherlands
HERMEQ Netherlands HERMEQ France
HERMEQ France HERMEQ DACH
HERMEQ DACH